Antistatic Shoes: Protecting Against Static Discharge
What They Do:
Antistatic shoes are engineered to prevent the buildup of static electricity on the wearer’s body. They work by dissipating static charges safely to the ground through conductive or dissipative materials in the sole. This reduces the risk of sudden electrostatic discharges (ESD), which can damage sensitive electronics or ignite flammable materials.
Key Features:
- Designed to meet resistance standards (typically 10^5 to 10^11 ohms) to control static dissipation.
- Often used in industries like electronics manufacturing, laboratories, or cleanrooms.
- Focus on protecting equipment, not the wearer, from static-related harm.
Limitations:
- Do not protect against electric shocks from live circuits or high-voltage sources.
- Not suitable for environments with exposed electrical hazards.
Electrical Hazard (EH) Rated Safety Shoes: Shielding Against Live Circuits
What They Do:
EH-rated safety shoes are specifically built to reduce the risk of electric shock in environments with live electrical sources. They incorporate insulating materials (e.g., non-conductive soles) to limit the flow of electricity through the body if the wearer accidentally contacts an energized circuit.
Key Features:
- Tested to withstand specific voltages (standards vary by region, e.g., ASTM F2413-18 in the U.S.).
- Common in industries like construction, utility work, or electrical maintenance.
- Focus on protecting the wearer from injury or fatal shocks.
Limitations:
- Not designed to prevent static buildup—may even retain static charges in some cases.
- Do not guarantee 100% protection in extreme high-voltage scenarios (always pair with other PPE).
Key Differences at a Glance
| Feature | Antistatic Shoes | EH-Rated Shoes |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Prevent static buildup/discharge | Protect against electric shock |
| Protection Focus | Equipment (e.g., electronics) | Wearer (from live circuits) |
| Voltage Handling | N/A (static only) | Rated for specific voltages |
| Common Industries | Electronics, pharmaceuticals | Construction, electrical utilities |
| Material Design | Conductive/dissipative soles | Insulated, non-conductive soles |
Choosing the Right Shoe for Your Job
- Assess Your Environment:
- Use antistatic shoes if working with static-sensitive devices (e.g., microchips, medical devices) or in explosive atmospheres.
- Opt for EH-rated shoes if exposed to live wires, panels, or high-voltage equipment.
- Check Compliance Standards:
- Look for certifications like ASTM (U.S.) or EN (Europe) to ensure the shoes meet safety requirements.
- Never Assume Interchangeability:
Wearing antistatic shoes in an EH environment (or vice versa) can lead to catastrophic risks.
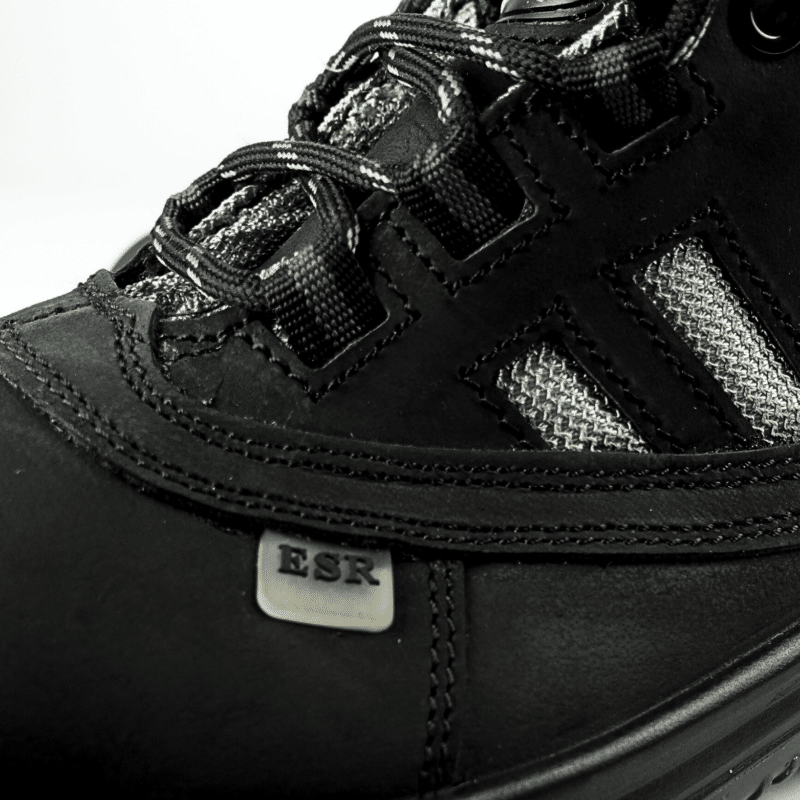
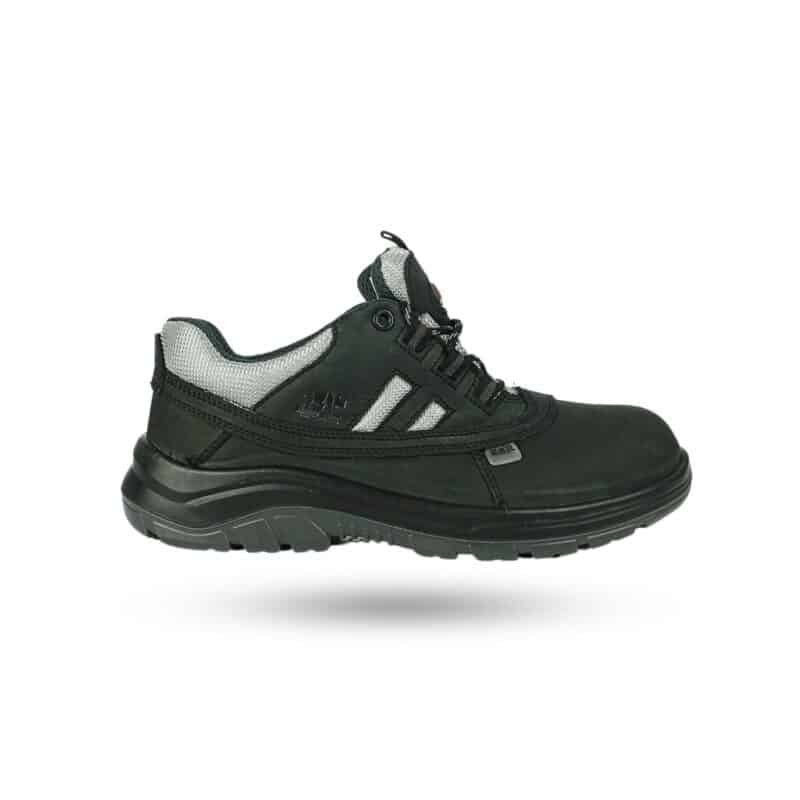
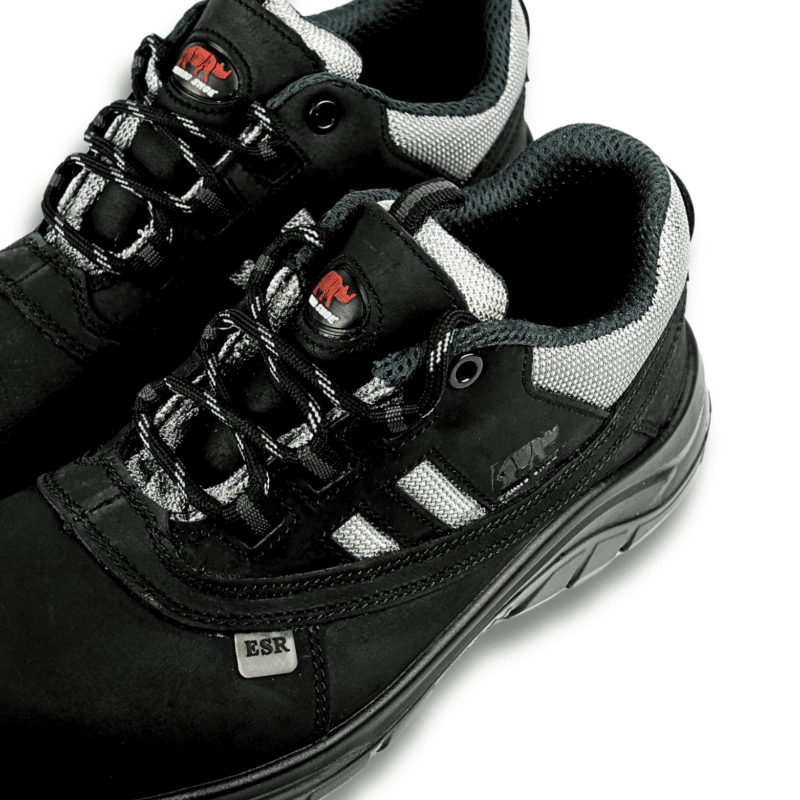



Looking for reliable Electrical Hazard (EH) protection without compromising on comfort? The RHINO SHOE EH101KP from the VoltGuard Series combines cutting-edge safety with premium design. Engineered to withstand up to 18,000 volts and compliant with ASTM F2413-18 standards, these shoes feature a lightweight fibreglass toe cap, anti-penetration midsole, and a water-resistant buffalo leather upper for durability. The oil- and chemical-resistant outsole ensures traction in hazardous environments, while the breathable mesh lining keeps feet cool during long shifts. Available in EU sizes 35–48, the EH101KP is built for safety professionals who demand uncompromising protection and all-day comfort. Step into safety—choose RHINO SHOE.
Final Thoughts
While both antistatic and EH-rated shoes address electrical safety, their applications are worlds apart. Antistatic footwear safeguards delicate equipment from static interference, whereas EH-rated boots prioritize worker safety in energized environments. Always consult safety guidelines and conduct a workplace hazard assessment to ensure you—and your equipment—stay protected.
For more updates on safety news and insights, visit our website at Safetyware.
Any Questions? Contact Us:
📩 Email: [email protected]
🌐 Website: www.safetyware.com
📞 Contact us: WhatsApp
